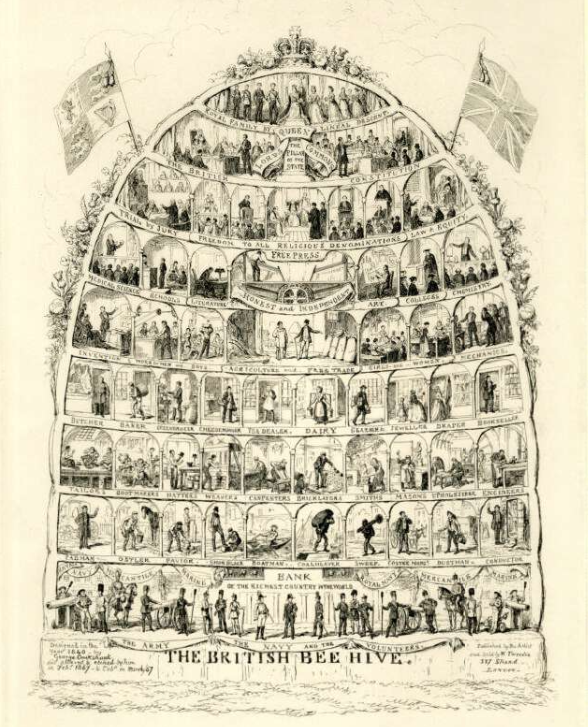
The Victorian era, like any other ancient time, had a peculiar class system that divided the social setting. It was based on power, riches, working and living conditions. Society was divided into Upper Class, Middle Class, and Lower Class, also known as the Working Class.
People belonging to the royal family, aristocrats, nobles, business owners, and wealthy families working in the royal courts were classed into the Upper Class. They were in powerful positions, had the utmost authority, had lavish lifestyles and enjoyed exceptional facilities.
Whereas, the middle class included either owned or managed business empires or the merchants. They were classified by earned wealth and not inherited wealth and lived a pretty sound life as well.
Lastly, the working class resided at the lowest level of the hierarchy. They were mainly labored workers who lacked money and hence, had a poor way of living.
The class system was also classified based on the clothes they wore. The Victorian era fashion trend during the Victorian Era was the expression of the estate one belonged. The elaborate pieces were worn by the women belonging to the upper class, middle class women wore modest dresses, and the women belonging to lower class wore what they could afford.
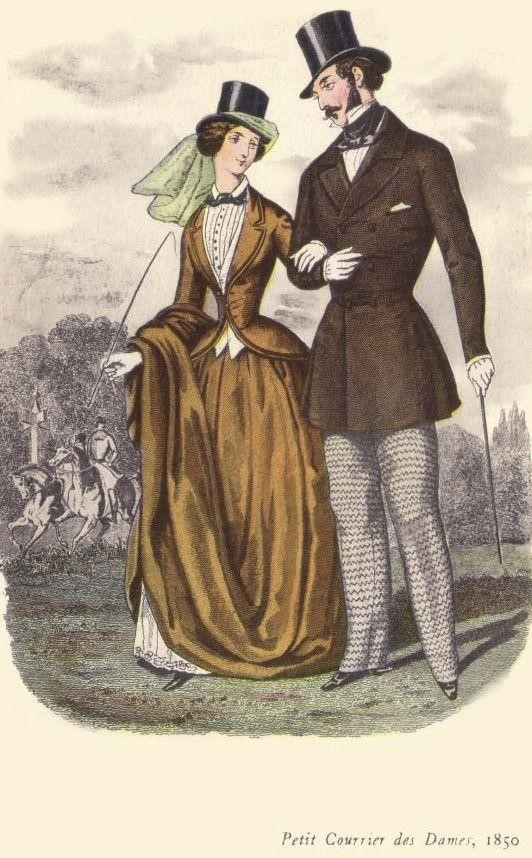 HOW WAS LIFE FOR THE UPPER CLASS?
HOW WAS LIFE FOR THE UPPER CLASS?
Property, rent, and interest provided income to the very small and very rich upper class. The upper class possessed titles, riches, land, or all three; they controlled local, national, and imperial politics; and they held the majority of the land in Britain.
The upper class inherited royals. It consisted of aristocrats, and all the titled people like the ones from the royal families, Lords, and Ladies, Earls, Dukes, and Duchesses. They did not have to work for generations and could afford to live a luxurious life. There were also business owners who had large-scale mining or shipping industries. As they inherited massive wealth from their previous generations, it gave them great access and authority. They were provided with inherited seats in the House of Lords. This gave them the power to vote on political affairs as well.
The education of the upper class was uncompromised, with the best tutors provided. The finest education and their royal background were always a plus point for them wherever they went. Usually, the upper-class boys were sent to boarding school at a very young age. The girls generally stayed home and received education from a governess. The eldest son was taught to run the family business and take care of the employees and their younger siblings. The younger ones went off to the army, navy, or church. The girls were taught etiquettes and mannerisms suitable for their status. They were expected to marry a man from similar backgrounds and start a family soon.
HOW WAS LIFE FOR THE MIDDLE CLASS?
Thrift, responsibility, and self-reliance were significant components of Victorian middle-class culture that could be used to characterize a society where individual tenacity and energy were required for success.
Although very few families belonged to the middle class, it was a pleasant life for the middle class in the Victorian era. The middle class was different from the upper class in terms of the history of their wealth. The wealth they had was earned wealth, as in they either owned or managed large businesses and collected a pretty good amount of wealth.
The industrial revolution brought a massive transition for the people of the Middle Class in terms of increased job opportunities and decent earnings. This transformed their way of living and their education as well. Their class consisted of merchants who were involved in trading goods for money. For the purpose of trade, they owned ships used to trade British goods for Indian goods like tea, coffee, and spices. They sold these products back in Britain and made huge profits out of it. They employed captains and crews and laborers and sufficed their livelihood. Similarly, the factory owners employed hundreds of laborers.
Doctors, lawyers, teachers, engineers, and bankers were some of the other professions of the middle class. They were paid very well, lived a pleasant life, and could afford properties. As the work opportunities started to increase among this class, it soon became the most populated class with abundant wealth.
Their children were also sent to boarding schools, where boys were taught to run the family business. The girls here as well were taught proper etiquette and trained to become good wives to a man of similar backgrounds and run a family.
 HOW WAS LIFE FOR THE LOWER CLASS?
HOW WAS LIFE FOR THE LOWER CLASS?
People from the working class were sometimes forced to live in confined poor quality homes, and families were frequently crammed into a single room. The industrial revolution resulted in overcrowding, which led to poor public health.
The working class ranks in the lowest part of the social hierarchy and is sub-categorized into skilled and unskilled workers. This class summed up the majority of the Victorian-era population. They are not included in political affairs and have a very poor lifestyle. They had a low supply of food, and due to their poor background, most of their children worked for extra family income. Even women had to work despite having children.
Laborers, sailors, fishermen, mine workers, and servants were included in their job type and paid on an hourly basis. The family would be forced to live on the streets if the primary income generator died due to a lack of money. Most of them lived in rented houses, and their houses were as big as they could earn. Most of them lived in a single room for an entire family.
Education was merely an option for the working class children, and they got married to people of their own background, creating a never-ending cycle of poverty. Still, the lower-class farmers tried to provide their daughters with an education along with the boys. The boys lived in hostels as they gained their education, and schools were built specifically for farmers.
During the industrial revolution. Most of the skilled workers got an opportunity to work in their craft and uplevel their status on some levels. However, the unskilled workers could never rise to a good life as they continued working as laborers and servants for the upper and middle-class people. This resulted in a rough life for the working class, and was hit by an even worse form of poverty. They lost all their previous rights as citizens and had little to no independence. Their income was unstable, and the little money they earned was barely enough to sustain their everyday life.
Conclusion
Hence, it was mainly the wealth that defined a person’s class during the Victorian era in Britain. More money meant a more lavish life and more access to various opportunities. Each system had its own rules. However, these rules started to fumble as the Victorian era progressed.
